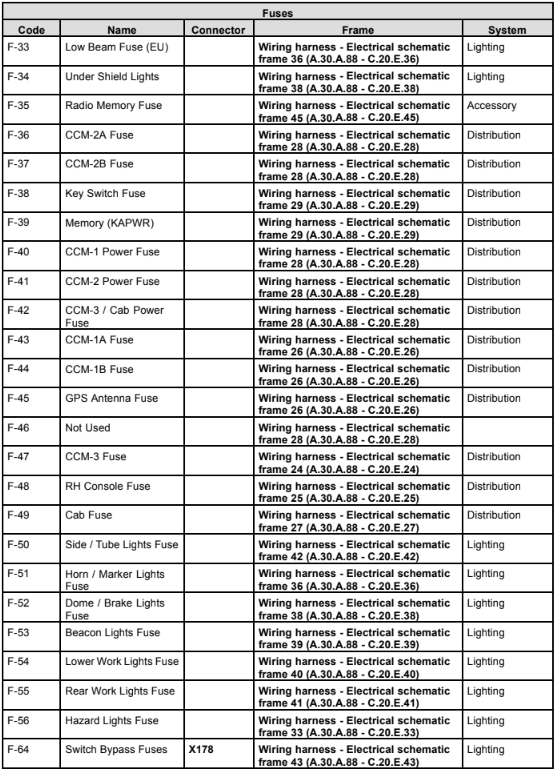
CASE AFX 8010 Fuses and Ralay

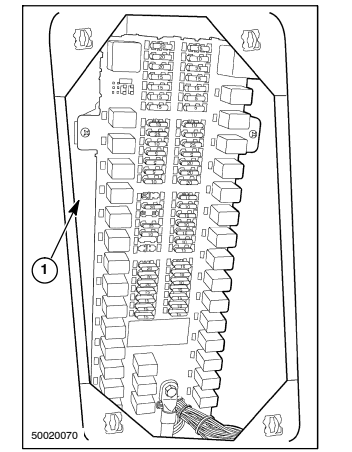
FUSES
Fuses protect circuits with thin pieces of metal and
wire which heat up and melt to open up the circuit
when too much current flows through them. The
combine fuse panel, 1, is located in the left rear
corner of the cab, behind a removable panel.
Fuses are used to protect the circuit from overload.
This can occur in the event of a short circuit or by
connecting equipment which demands a current
greater than the circuit is designed to carry.
There are several types of fuses, but they all consist
of a metal conductor which is capable of carrying a
limited current. If the specified current is exceeded
then the metal conductor will overheat, causing it to
melt and break. This will in turn cause an open circuit.
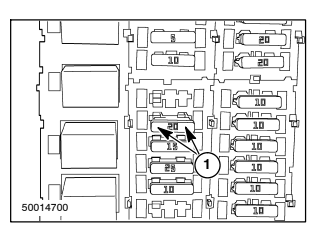
The rating of the fuse relates to the current that the
fuse can carry continuously.
If a fuse blows, it must be replaced with a fuse of the
correct rating, and if it blows again, then the cause
must be investigated.
A fuse may be tested by checking continuity across
the fuse on the two exposed terminals,
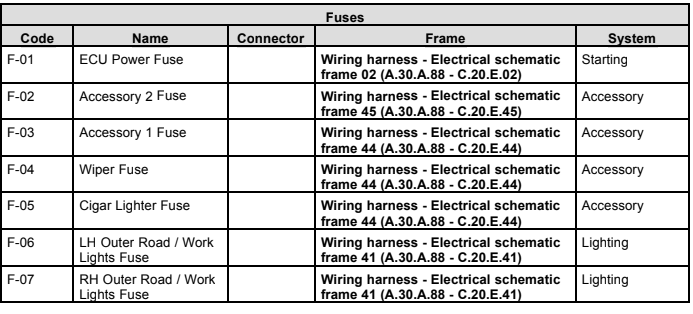
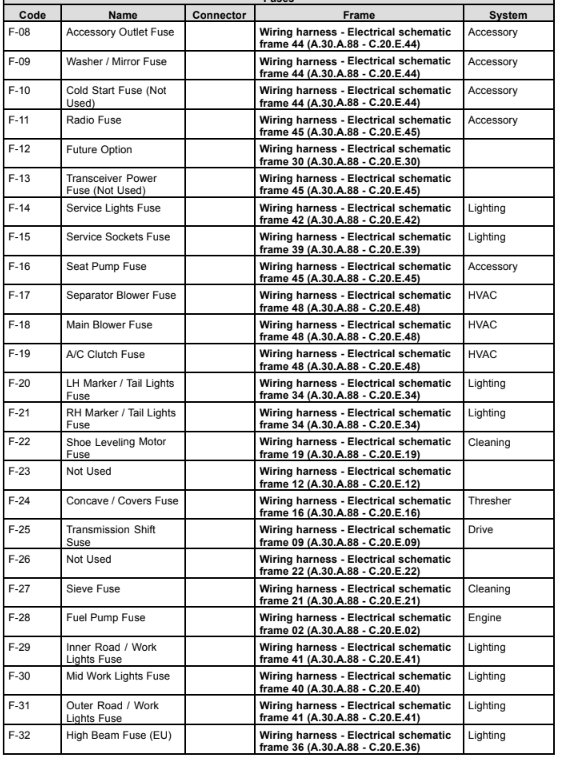
Wiring harness - Electrical schematic frame 01 (A.30.A.88 - C.20.E.01)
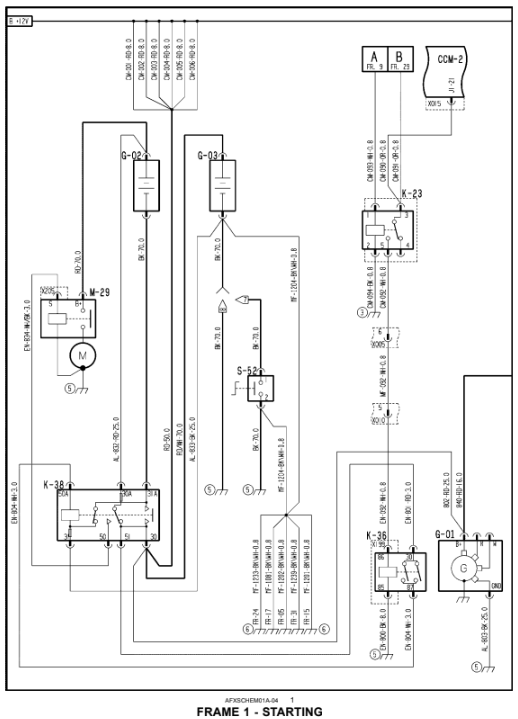
G-01 Alternator G-02 Front Battery G-03 Rear Battery
K-23 Neutral Start Relay K-36 Start Relay K-38 24V Start Relay
M-29 24V Starter S-52 Battery Switch (EU) 7 = European Base Unit
8 = North American Base Unit
Wiring harness - Electrical schematic frame 02 (A.30.A.88 - C.20.E.02)
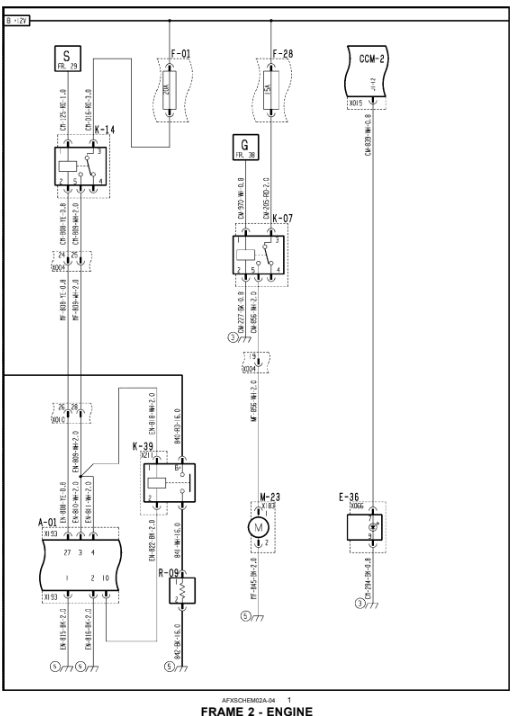
A-01 Iveco ECU E-36 Cold Start Indicator F-01 ECU Power Fuse
F-28 Fuel Pump Fuse K-07 Fuel Pump Relay K-14 ECU Power Relay
K-39 Grid Heater Relay M-23 Fuel Pump R-09 Engine Grid Heater
Wiring harness - Electrical schematic frame 44 (A.30.A.88 - C.20.E.44)

